Web hosting is a fundamental service that allows organizations and individuals to publish their websites and make them accessible to users worldwide through a unique URL (Uniform Resource Locator). Essentially, web hosting involves storing your website files on a high-end server machine with a unique IP address, enabling global access to your content.
As people increasingly depend on online solutions to meet their needs, having a reliable web presence has become crucial for businesses and individuals alike. However, with numerous hosting options available in the market, choosing the right type can be overwhelming due to technical terminology and blurred distinctions between different services.
Quick Decision Guide
Need help choosing quickly?
Just starting out? → Shared Hosting
Growing business with steady traffic? → VPS Hosting
WordPress site with high traffic? → Managed WordPress Hosting
Enterprise with high security needs? → Dedicated Server
Variable seasonal traffic? → Cloud Hosting
Quick decision guide based on your needs
Why Choosing the Right Hosting Type Is Critical
Your hosting choice extends far beyond simply providing a “place where your site lives.” The right hosting solution can significantly impact your website’s performance, security, and overall success. Here’s why it matters:
Performance and Reliability: Proper hosting ensures optimal website speed, stability, and uptime, directly affecting user experience and search engine rankings.
Workflow Optimization: Modern hosting solutions offer automated features like one-click setups and auto-updates that streamline website creation and maintenance processes.
Security and Data Protection: Quality hosting providers include essential security tools such as daily backups, built-in protection solutions, and monitoring systems that safeguard your data and prevent costly downtime or data loss.
Enhanced User Experience: Advanced features like Content Delivery Networks (CDN) and caching tools significantly improve website loading times and overall performance.
Cost Efficiency: The right hosting choice can reduce operational costs through automation, bundled services, and scalable pricing models that match your actual usage needs.
Given that hosting decisions can directly influence your website’s success and, consequently, your business outcomes, understanding the different types of hosting and their specific use cases is essential for making an informed decision.
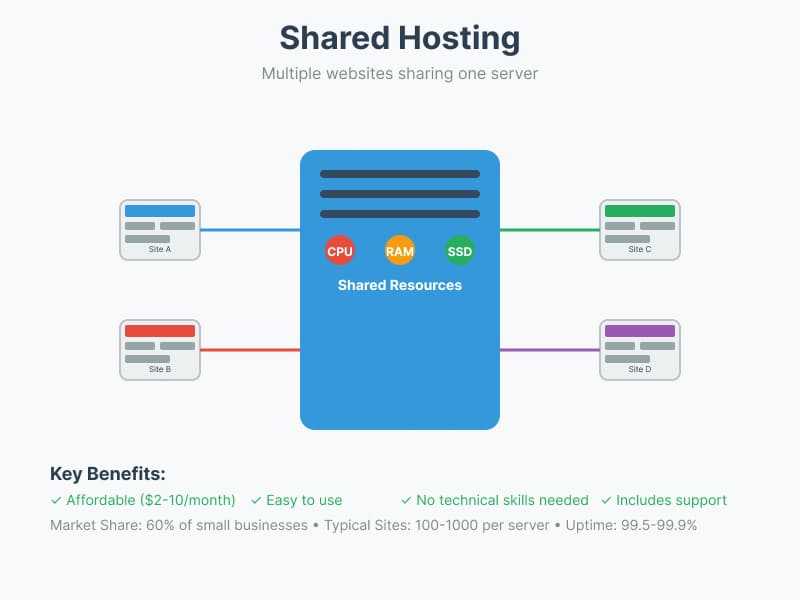
1. Shared Web Hosting
Shared hosting is a web hosting model where multiple websites share the resources of a single physical server. Each website receives a portion of the server’s CPU time, memory, and disk space.
Shared hosting dominates the web hosting landscape, particularly among small businesses where it accounts for approximately 60% of all hosting choices. This popularity stems largely from its affordability, with plans typically ranging from $2 to $10 per month. The shared hosting model contributes significantly to the overall web hosting market, which is projected to reach $159.9 billion in revenue by 2024. Most shared hosting providers maintain uptime levels between 99.5% and 99.9%, making it a reliable option for basic website needs.
Technical Specifications:
- Typical number of sites per server: 100-1000
- Disk space allocation: 5-100 GB
- Monthly bandwidth: 50-500 GB
- Average response time: 500-2000 ms
Advantages:
- Most affordable hosting option
- Easy setup and user-friendly interface
- Pre-installed control panels (cPanel, Plesk)
- Provider technical support included
- Automatic system updates
Disadvantages:
- Performance depends on neighboring sites’ activity
- Limited customization options
- Potential security vulnerabilities due to shared resources
- Possible slowdowns during peak traffic periods
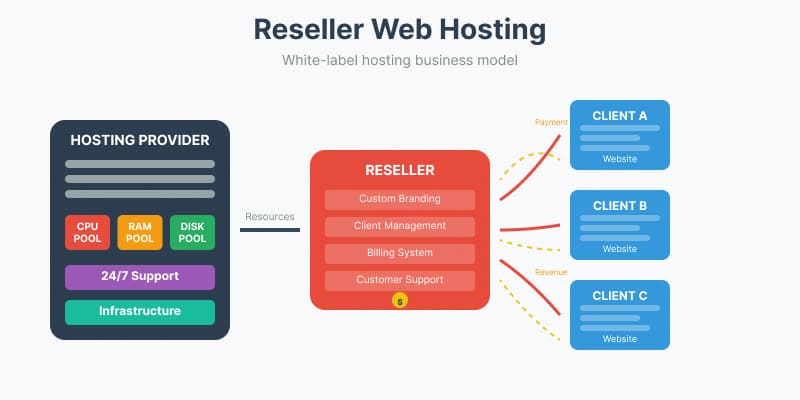
2. Reseller Web Hosting
Reseller hosting is a business model where the primary provider offers hosting resources to intermediaries for further resale to end users.
The reseller hosting market represents a niche but growing segment, accounting for approximately 8% to 12% of the total hosting market. This business model attracts entrepreneurs and web developers looking to start their hosting ventures with minimal investment. Monthly costs for reseller packages typically range from $15 to $50, while profit margins can be quite attractive, often reaching 50% to 70%. Interestingly, 78% of resellers expand their business by offering additional services beyond basic hosting, creating comprehensive digital service packages.
Technical Characteristics:
- Allocated resources: 50-500 GB disk space
- Bandwidth allocation: 500 GB – 5 TB monthly
- Number of accounts: 25-unlimited
- White-label branding options available
Advantages:
- Low initial investment for hosting business
- More flexibility than shared hosting
- White-label technical support from hosting provider
- Revenue generation opportunity through reselling
- No need to manage technical infrastructure
Disadvantages:
- Risk of significant damage during server issues
- Responsibility for providing customer support
- Slow data recovery during failures
- Dependency on primary provider’s reliability
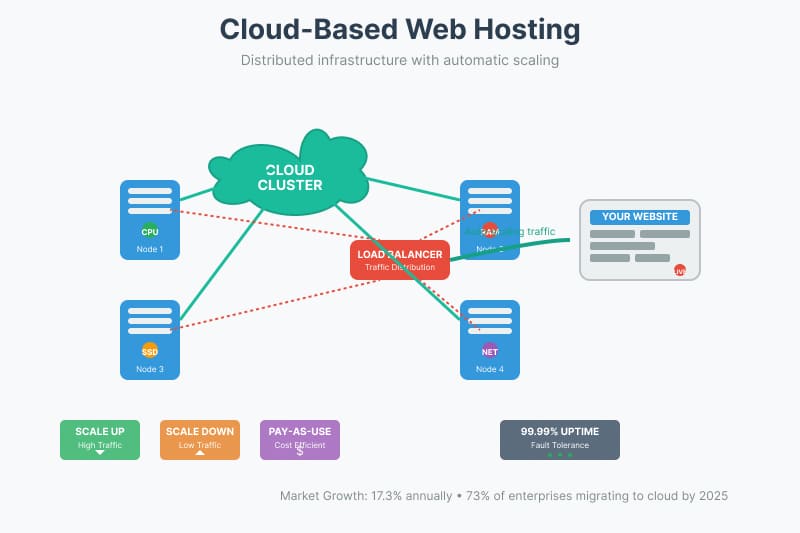
3. Cloud-Based Web Hosting
Cloud hosting utilizes a cluster of servers to provide services based on individual needs, distributing resources across multiple machines for enhanced reliability and scalability.
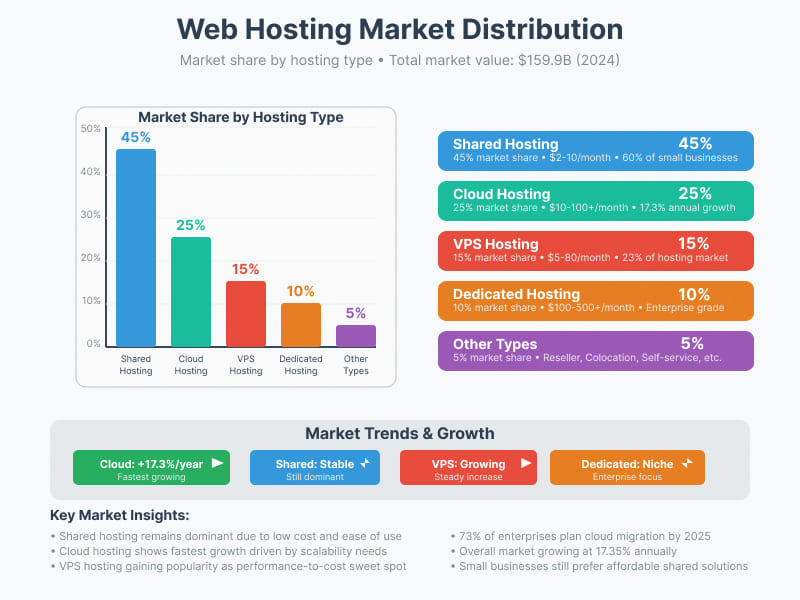
Cloud hosting represents one of the fastest-growing segments in the hosting industry, with the market expanding at an impressive annual rate of 17.3%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for scalable and reliable hosting solutions. Pricing for cloud hosting typically ranges from $10 to over $100 per month, depending on resource usage and traffic patterns. The pay-as-you-use model appeals to businesses with variable traffic, as costs scale with actual consumption. Cloud hosting providers typically achieve exceptional uptime rates of 99.99%, which translates to just 52 minutes of downtime annually. Looking ahead, 73% of enterprises plan to migrate more workloads to cloud platforms by 2025, indicating continued growth in this sector.
Technical Architecture:
- Multiple server cluster infrastructure
- Load balancing across nodes
- Automatic resource scaling
- Redundant data storage across multiple locations
Advantages:
- Easy resource scalability
- Pay-as-you-use pricing model
- High fault tolerance and reliability
- Instant access to additional resources
- More affordable than dedicated servers
- Superior uptime compared to traditional hosting
Disadvantages:
- Can be more complex to configure
- Costs can fluctuate significantly with traffic spikes
- Requires understanding of cloud architecture
- Potential vendor lock-in issues
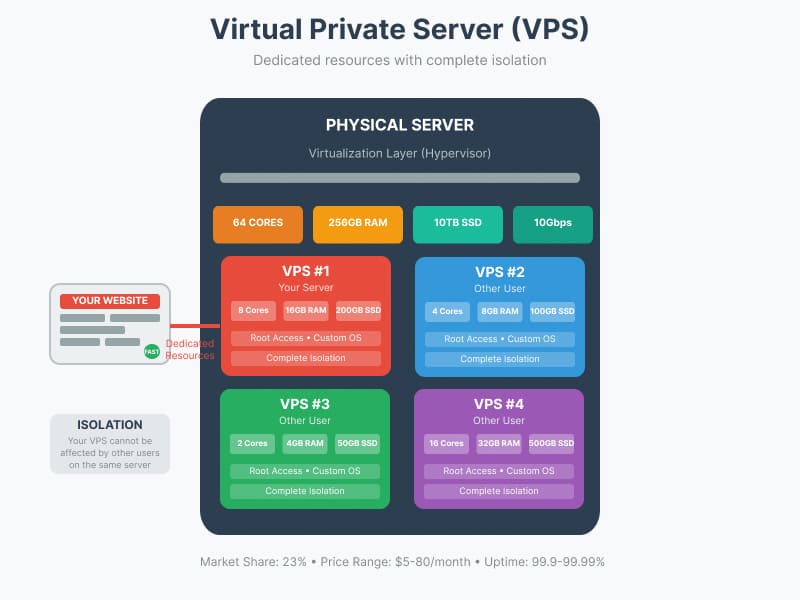
4. Virtual Private Server (VPS)
VPS hosting provides a virtual server with dedicated resources on a physical server, isolated from other users through virtualization technology.
VPS hosting has gained significant traction in recent years, now representing 23% of the hosting market share. This growth is driven by the balance it offers between affordability and performance. VPS solutions have become increasingly accessible, with entry-level plans now available starting at just $4 per month, though most quality VPS services range from $5 to $80 monthly. VPS providers typically maintain excellent uptime standards between 99.9% and 99.99%, offering reliability that bridges the gap between shared hosting and dedicated servers.
Technical Specifications:
- Dedicated RAM: 1-32 GB typical range
- CPU cores: 1-8 cores allocated
- Storage: 20-500 GB SSD/NVMe
- Bandwidth: Usually unlimited or 1-10 TB
Advantages:
- Dedicated RAM and CPU allocation
- Isolation from other websites
- More stable performance than shared hosting
- Enhanced security compared to shared hosting
- Lower cost than dedicated servers
- Root access and customization options
Disadvantages:
- Requires technical knowledge for management
- Higher cost than shared hosting
- Need for server administration skills
- Potential for misconfiguration
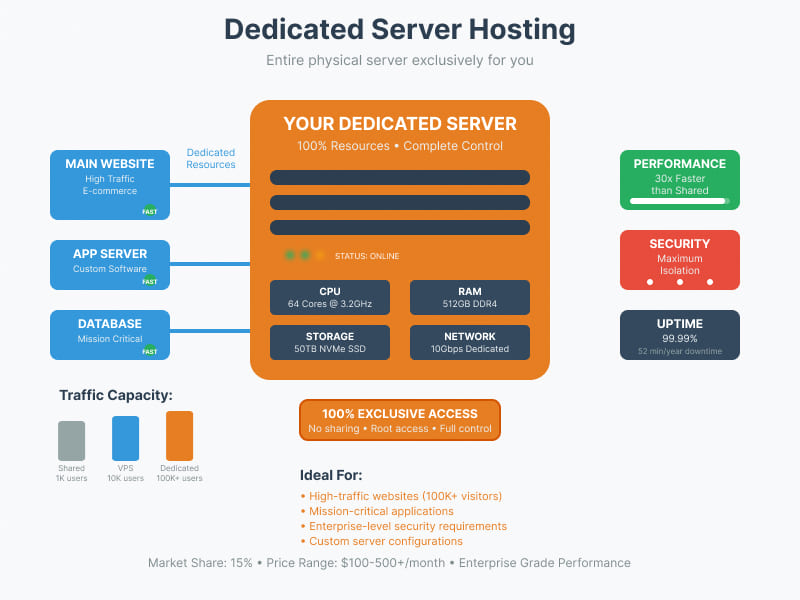
5. Dedicated Web Server
Dedicated hosting provides an entire physical server exclusively to one client, offering maximum performance and control.
Dedicated servers represent a premium hosting segment, accounting for approximately 15% of the hosting market. Despite their higher cost, ranging from $100 to $500 or more per month, dedicated servers are essential for high-traffic websites and enterprise applications. These servers can handle between 10,000 to 100,000 or more concurrent visitors, making them capable of processing 30 times more traffic than shared hosting environments. Dedicated hosting providers typically maintain exceptional uptime standards between 99.95% and 99.99%, ensuring minimal service interruptions for critical business operations.
Performance Metrics:
- Full server resources available
- CPU: 4-64 cores typical
- RAM: 16-512 GB standard range
- Storage: 1-50 TB capacity
- Network: 1-10 Gbps connection
Advantages:
- Maximum performance and speed
- Complete control and root access
- Can handle 30x more traffic than shared hosting
- Guaranteed security and isolation
- Fast page loading times
- Custom server configuration possible
Disadvantages:
- High cost investment
- Requires significant technical expertise
- Need for self-administration
- Responsible for security and maintenance
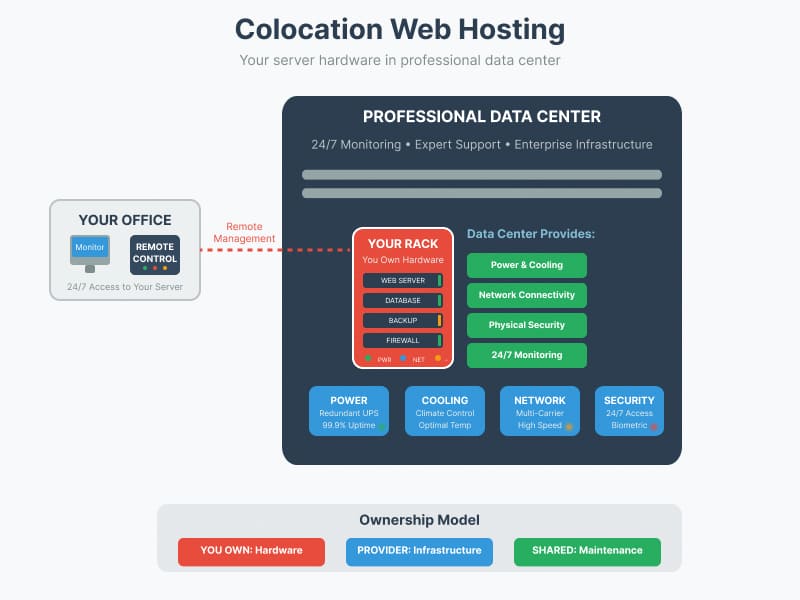
6. Colocation Web Hosting
Colocation involves owning your server hardware but housing it in a data center facility provided by a hosting company.
The colocation market has shown steady growth, reaching a valuation of $62.3 billion in 2024. This hosting model appeals particularly to medium and large companies seeking to reduce operational expenses while maintaining control over their hardware. Colocation services typically cost between $50 and $300 per server monthly, with most facilities providing 1 to 5 kilowatts of power allocation per rack. Customer satisfaction in the colocation sector is notably high, with 95% of clients reporting improved reliability compared to their previous hosting arrangements.
Infrastructure Features:
- Customer-owned hardware
- Data center facilities and infrastructure
- Professional cooling and power systems
- Network connectivity and bandwidth
- Physical security and monitoring
Advantages:
- Complete control over hardware specifications
- Expert data center support and monitoring
- Reduced operational expenses
- Easy scalability options
- 24/7 server access
- Professional infrastructure without full investment
Disadvantages:
- Responsibility for hardware, backups, and component replacement
- High initial hardware investment
- Lower operational efficiency for end users
- Need for hardware expertise
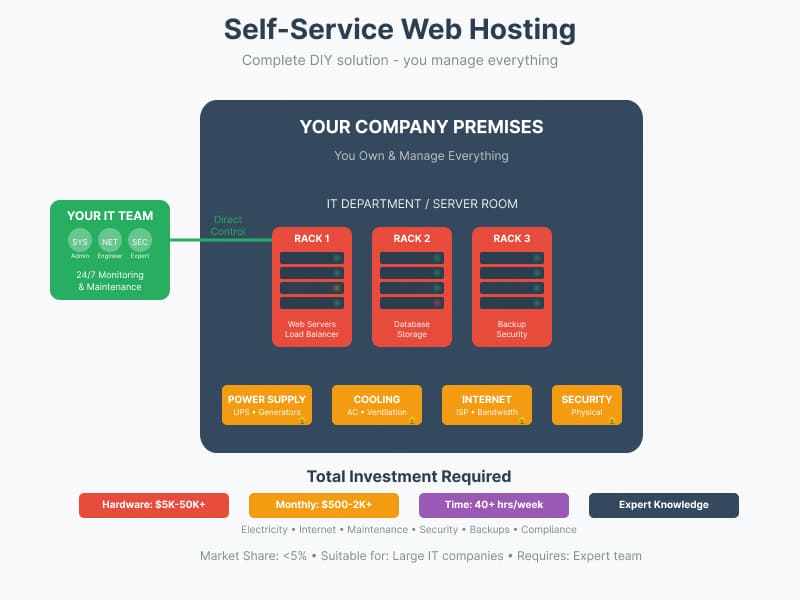
7. Self-Service Web Hosting
Self-service hosting is a completely autonomous solution where you purchase, install, and manage all equipment independently.
Self-service hosting represents a highly specialized niche, chosen by less than 5% of businesses due to its demanding technical requirements and substantial financial investment. Organizations opting for this approach typically face initial investments ranging from $5,000 to $50,000 or more for enterprise-grade setups. Beyond the initial hardware costs, operational expenses can reach $500 to $2,000 monthly, covering electricity, internet connectivity, and ongoing maintenance. This hosting model demands significant time commitment, requiring 40 or more hours weekly for proper system management and monitoring.
Infrastructure Requirements:
- Server hardware purchase and maintenance
- Network infrastructure setup
- Power and cooling systems
- Security implementation
- Backup solutions
Advantages:
- Maximum control over entire system
- No monthly payments to hosting providers
- Complete independence from third parties
- Custom hardware configurations
- No vendor dependencies
Disadvantages:
- Requires exceptional technical expertise
- Need to provide: cooling, power, internet connectivity, security
- High initial capital investment
- Full responsibility for system administration
- 24/7 monitoring and maintenance requirements
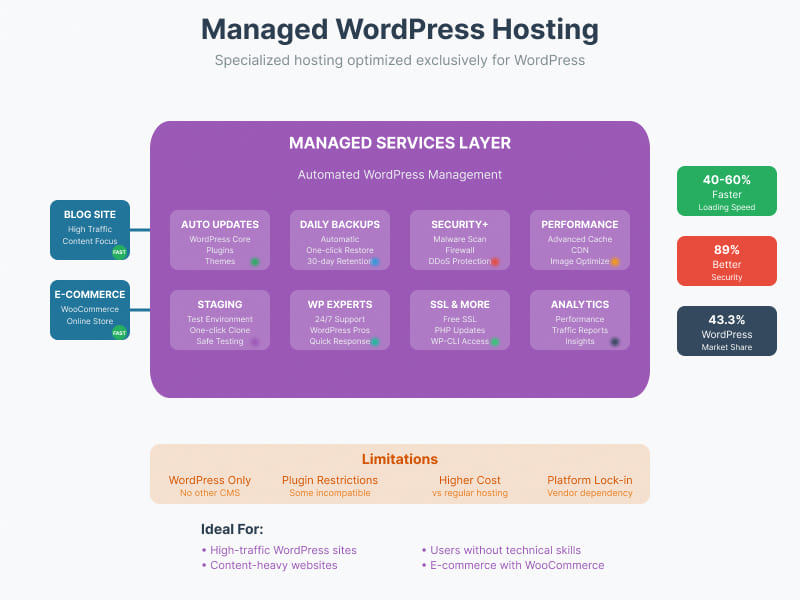
8. Managed WordPress Hosting
Specialized hosting optimized exclusively for WordPress websites, providing enhanced performance and WordPress-specific features.
Managed WordPress hosting serves a substantial market, given that WordPress powers 43.3% of all websites globally. This specialized hosting segment commands premium pricing, typically ranging from $15 to $200 or more per month, reflecting the value-added services it provides. The performance benefits are significant, with managed WordPress hosting delivering average speed improvements of 40% to 60% compared to standard hosting solutions. Security is another major advantage, with 89% of managed WordPress users reporting enhanced security compared to their previous hosting arrangements.
WordPress-Specific Features:
- Automatic WordPress updates
- WordPress-optimized server configuration
- Advanced caching mechanisms
- WordPress security hardening
- Staging environments for testing
Advantages:
- Automatic and manual backup systems
- Automatic WordPress core updates
- Performance optimization for WordPress
- Enhanced caching capabilities
- Improved security measures
- Staging environment for testing changes
- WordPress expert support
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility (WordPress only)
- Incompatibility with certain plugins
- Higher cost than standard hosting
- Vendor lock-in to WordPress platform
- Restrictions on custom server configurations
9. Free Hosting
Free hosting services provide basic web hosting functionality at no cost, typically supported through advertising revenue.
Free hosting occupies a small but notable segment of the market, accounting for less than 10% of active websites. Despite being free, these services face significant limitations in reliability and performance, typically maintaining uptime levels between 95% and 98%, considerably lower than the 99.9% standard of paid hosting services. Storage restrictions are severe, usually limited to between 100 MB and 5 GB, while monthly bandwidth caps range from 1 to 10 GB. Interestingly, the conversion rate from free to paid hosting is quite high, with 78% of free hosting users upgrading to paid plans within their first 12 months as their needs outgrow the basic limitations.
Service Limitations:
- Extremely limited resources
- Subdomain-based hosting
- Provider advertising insertion
- Minimal technical support
- Basic functionality only
Advantages:
- Completely free of charge
- Suitable for learning web development
- Quick start for test projects
- No financial investment required
- Basic website building tools included
Disadvantages:
- Provider advertising displayed on websites
- Severely limited resources (storage, bandwidth)
- Subdomain instead of custom domain
- Minimal or no technical support
- Limited functionality and features
- Poor reliability and uptime
- Risk of sudden service termination
- No SSL certificates or security features
Comparative Analysis Tabl
| Hosting Type | Cost Range | Scalability | Technical Knowledge Required | Primary Use Cases |
| Shared Hosting | $2-10/month | Low | Minimal | Personal blogs, small business websites, portfolios |
| Reseller Hosting | $15-50/month | Medium | Low-Medium | Hosting business startups, web developers, agencies |
| Cloud Hosting | $10-100+/month | Very High | Medium | Variable traffic sites, seasonal businesses, growing projects |
| VPS Hosting | $5-80/month | High | Medium-High | E-commerce sites, medium traffic websites, applications |
| Dedicated Server | $100-500+/month | Medium | High | High-traffic websites, enterprise applications, gaming servers |
| Colocation | $50-300/month + hardware | High | High | Medium-large companies, cost optimization, custom hardware needs |
| Self-Service | $500-2000+/month operational | Very High | Expert | Large enterprises, IT companies, maximum control requirements |
| Managed WordPress | $15-200+/month | Medium | Low | WordPress sites, blogs, content-heavy websites |
| Free Hosting | $0 | Very Low | Minimal | Learning projects, personal experiments, temporary sites |
Market Distribution
Based on current market analysis:
- Shared Hosting: 45% market share
- Cloud Hosting: 25% market share
- VPS Hosting: 15% market share
- Dedicated Hosting: 10% market share
- Other Types: 5% market share
The hosting industry continues to evolve with an expected annual growth rate of 17.35%, driven primarily by increased cloud adoption and the growing need for scalable hosting solutions.
How to Choose the Right Hosting Type: Practical Decision Framework
Making the right hosting choice requires evaluating several key factors. Here’s a practical framework to guide your decision:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Needs
- Website Type: Blog, e-commerce, corporate site, or application
- Traffic Volume: Current visitors per month and expected growth
- Technical Skills: Your team’s ability to manage servers
- Budget: Monthly hosting budget and acceptable cost scaling
Step 2: Consider Growth Trajectory
- 6-Month Outlook: Expected traffic and feature requirements
- 1-Year Projection: Scaling needs and potential expansion
- Long-term Vision: Enterprise features or global reach requirements
Step 3: Evaluate Critical Requirements
- Performance Needs: Page load speed requirements and visitor capacity
- Security Level: Data sensitivity and compliance requirements
- Customization: Need for custom server configurations or software
- Support Expectations: Level of technical assistance required
Migration Considerations
Most hosting types allow for upgrades as your needs grow:
- Shared → VPS: Common upgrade path as traffic increases
- VPS → Dedicated: Natural progression for high-traffic sites
- Traditional → Cloud: Migration for better scalability and reliability
- Standard → Managed: Upgrade for specialized platform optimization
Red Flags: When Your Current Hosting Isn’t Working
- Frequent downtime or slow loading times
- Unable to handle traffic spikes
- Security vulnerabilities or breaches
- Inadequate customer support response
- Outgrowing resource limitations
- Excessive costs for required features
Expert Recommendation: Start with a hosting type that meets your current needs with 20-30% growth capacity. This approach avoids over-investment while ensuring room for expansion without immediate migration pressure.
Conclusion: Making Your Hosting Decision with Confidence
Choosing the right web hosting solution is one of the most critical decisions you’ll make for your online presence. As we’ve explored, each hosting type serves distinct purposes and caters to different stages of website growth and business requirements.
Key Takeaways
Start Small, Scale Smart: Most successful websites begin with shared or managed WordPress hosting and evolve as their needs grow. There’s no shame in starting with a $5/month solution if it meets your current requirements.
Performance Matters More Than Ever: With Google’s emphasis on Core Web Vitals and user experience, your hosting choice directly impacts your search rankings and user satisfaction. A slow website on cheap hosting can cost you more in lost opportunities than investing in quality hosting from the start.
Security Is Non-Negotiable: Cyber threats continue to evolve, making security features like automated backups, SSL certificates, and malware protection essential rather than optional. The cost of a security breach far exceeds the price difference between basic and secure hosting.
Plan for Growth: The hosting market’s 17.35% annual growth rate reflects businesses’ increasing digital demands. Choose a provider that offers clear upgrade paths and can scale with your success.
Final Recommendations by Use Case
For Beginners and Small Businesses: Start with shared hosting ($2-10/month) or managed WordPress hosting ($15-50/month) depending on your platform. Focus on providers with strong customer support and easy-to-use control panels.
For Growing Businesses: VPS hosting ($5-80/month) offers the best balance of performance, control, and cost. It provides room for traffic growth while maintaining affordability.
For Established Enterprises: Dedicated servers ($100-500+/month) or enterprise cloud solutions provide the performance, security, and customization needed for mission-critical applications.
For Seasonal or Variable Traffic: Cloud hosting’s pay-as-you-use model ($10-100+/month) perfectly matches fluctuating demands without overpaying for unused resources.
The Bottom Line
Your hosting choice isn’t just about where your website lives—it’s about creating the foundation for your online success. Quality hosting enables faster loading times, better security, improved user experience, and ultimately, better business results.
Don’t let analysis paralysis prevent you from getting started. Choose a reputable provider that matches your current needs and budget, knowing you can always upgrade as you grow. The most expensive mistake isn’t choosing the wrong hosting initially—it’s waiting too long to launch your online presence while trying to make the “perfect” choice.
Remember: great websites are built, not born. Start with solid hosting that meets your needs today, focus on creating valuable content, and scale your infrastructure as your success demands it.
Ready to choose your hosting? Use our decision framework above, consider your specific requirements, and don’t hesitate to contact hosting providers directly with questions. Most reputable companies offer money-back guarantees, making it easier to try their services risk-free.
The web hosting landscape will continue evolving, but the principles remain constant: prioritize performance, security, and scalability, and choose providers who support your growth journey rather than just selling you a service.